
MRI Knee Scan or Magnetic Resonance Imaging Knee is a special type of scan that uses magnetic and radio waves to create a detailed image of the knee.
MFine offers you multiple lab options and an excellent discount of upto 50% for your MRI Knee in Chennai.
|
MRI Scan Knee In Chennai By MFine
|
Don’t pay the average market price for a Knee MRI in Chennai, which is above ₹18,200! Act now to save up to 50% with our limited-time offer of ₹2,750.
Request a callback by clicking the button below or calling us at ☏08068172507.
Our team is standing by to help you with any inquiries you may have.
Book your Knee MRI in Chennai for just ₹2,750 and receive a FREE online consultation with a doctor.
Knee MRI scan costs in Chennai
We’ve compiled the discounted pricing for the knee MRI scans that are commonly performed in Chennai. It’s important to note that these rates might be revised; to acquire the most current information, please get in touch with us.
| Center | MRP (in Rs) | MFine price (in Rs) |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Anna Nagar (Night Booking) | 2750 | 2750 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Kilpauk (Night Booking) | 2750 | 2750 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Vadapalani (Night Booking) | 2750 | 2750 |
| Proscans Diagnostics, Villivakkam | 3000 | 2900 |
| Proscans Diagnostics, Madipakkam | 3000 | 2900 |
| Scans World, Nungambakkam | 3500 | 2999 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Kilpauk | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Alwarpet | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Anna Nagar | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Alwar Thirunagar | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Tondiarpet | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Tambaram | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Vadapalani | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Porur | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Medavakkam | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Chromepet | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Madipakkam | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Villivakkam | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Kolathur | 3650 | 3557.5 |
| Aarthi Diagnostics, Ambattur | 3650 | 3557.5 |
|
Why Should I Book MRI Through MFine?
|
Exclusive Benefits with MFine
(1) Certified labs
Get access to over 600+ labs certified by NABL and NABH
(2) Same-day slot available
Get scans done on the same day
(3) Quick and convenient
Get reports in 12 hours and digital films in 15 – 20 minutes
(4) FREE Consultation
Post scans, consult a doctor for free to review your report
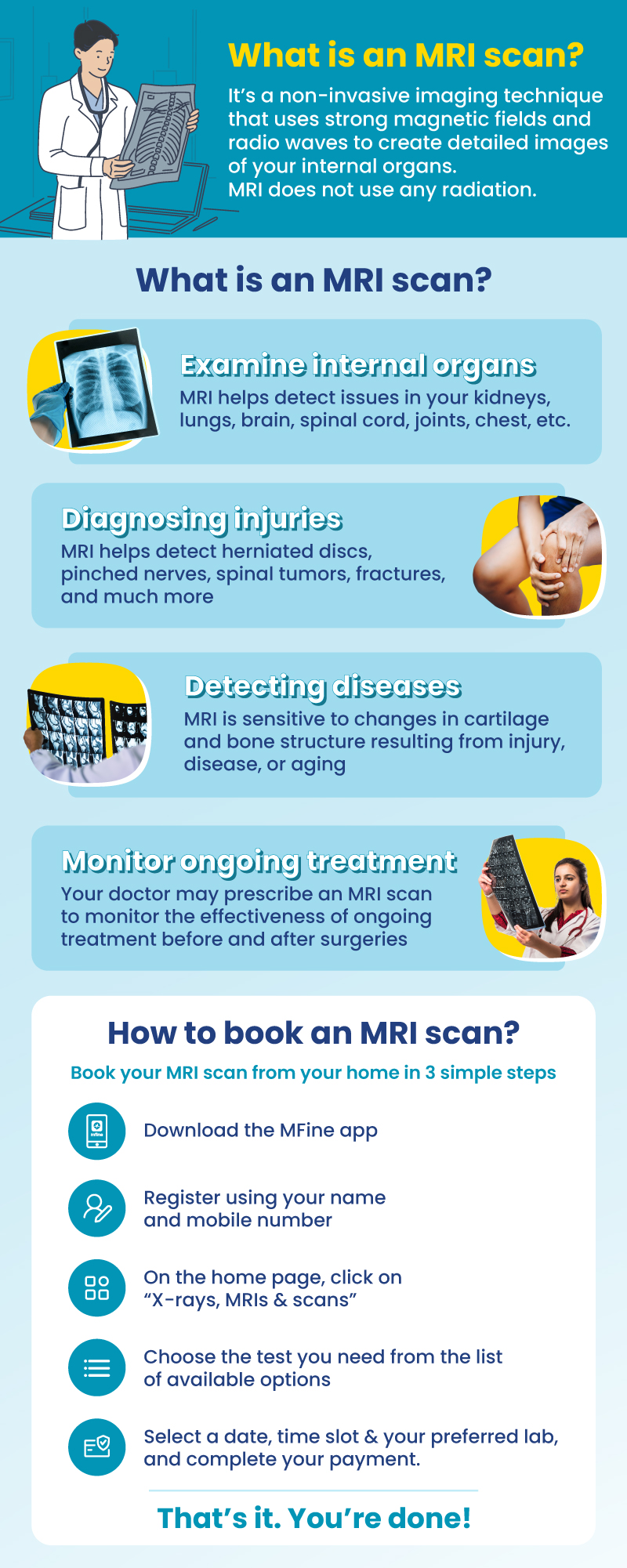
All about Knee MRI Scan
Your knee joint connects your thigh bone (femur), shin bone (tibia), and knee cap (patella). It allows you to do incredible things like walking, running, and jumping. But did you know that behind its simplicity lies a hidden network of bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and more, all working together to support and move your knee?
Sometimes, your knee can face problems, and to figure out what’s going on inside, doctors use a special tool called a knee MRI scan. Here, let’s explore the intricacies of your knee joint, the importance of knee MRI scans, why doctors order them, and what happens during the procedure.
Different components of the Knee Joint
- Bones:
- Femur (Thigh Bone): The big bone in your thigh that supports your knee and helps you move around.
- Tibia (Shin Bone): The larger of the two leg bones, keeping your knee steady when you stand and walk.
- Patella (Knee Cap): A small, flat bone in front of your knee joint that protects it and helps with knee movements.
- Cartilage:
- Meniscus: Two C-shaped cushions in your knee that act like shock absorbers during activities and keep your knee joint healthy.
- Articular Cartilage: Smooth, protective covering on the ends of your bones that allows your knee to move smoothly without friction.
- Ligaments:
- ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament): The important ligament in the middle of your knee that keeps it stable and prevents your shin bone from moving too far forward.
- PCL (Posterior Cruciate Ligament): Another ligament behind the ACL that stops your shin bone from moving too far backward.
- MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament): Found on the inside of your knee, it stops your knee from bending inward.
- LCL (Lateral Collateral Ligament): Located on the outside of your knee, it stops your knee from bending outward.
- Tendons:
- Quadriceps Tendon: Connects your thigh muscles to your knee cap, helping you straighten your leg.
- Patellar Tendon: Connects your knee cap to your shin bone, allowing you to jump and run.
- Muscles:
- Quadriceps: The muscles in the front of your thigh that work together to help you extend your knee and straighten your leg.
- Hamstrings: The muscles at the back of your thigh that bend your knee and help you with activities like walking and running.
- Gluteal Muscles (Glutes): The muscles in your buttocks that provide stability during weight-bearing activities.
- Joint Capsule: A thin, strong membrane surrounding your knee joint that helps keep it stable. It’s lined with synovial fluid, which keeps your knee lubricated for smooth movement.
- Bursae: Fluid-filled sacs that act like cushions, reducing friction between tissues in your knee and allowing them to move smoothly.
Why Knee MRI Scans are Important?
Knee MRI scans are essential tools used by doctors to diagnose knee issues accurately. By using strong magnets and radio waves, these scans create detailed pictures of what’s going on inside your knee. The significance of knee MRI scans includes:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Knee MRI scans help doctors identify various knee problems such as ligament tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL), meniscal tears, cartilage injuries, and fractures. These clear images help plan the right treatment.
- Evaluating Degenerative Conditions: Knee MRI scans are great for assessing conditions like osteoarthritis, allowing doctors to monitor your knee health and decide on the best treatments.
- Planning Surgeries: Before knee surgeries like ACL reconstruction or meniscal repair, knee MRI scans give crucial information about the extent of damage, helping surgeons plan successful procedures.
- Monitoring Recovery: After surgery or during recovery, knee MRI scans help doctors see how well your knee is healing and responding to treatment.
Reasons for Getting a Knee MRI Scan
Doctors may order knee MRI scans for various reasons, including:
- After an Injury: If you’ve had an accident or injury to your knee, a knee MRI scan can show the extent of the damage to bones, ligaments, cartilage, and soft tissues.
- Persistent Knee Pain: If you’ve been having ongoing knee pain, swelling, or trouble moving your knee, a knee MRI scan can help find out why.
- Sports Injuries: Athletes or people involved in sports can sometimes injure their knees. A knee MRI scan can help diagnose sports-related injuries and plan proper treatment.
- Chronic Knee Conditions: For conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis that affect the knee over time, knee MRI scans can help track the progress of the disease and guide treatment decisions.
- Unexplained Symptoms: If you have knee-related symptoms that other tests can’t explain, a knee MRI scan can provide a more detailed look to find the cause.
What to Expect During a Knee MRI Scan?
A knee MRI scan is a safe and painless procedure that usually takes between 30 to 60 minutes. Here’s what you can expect:
- Preparation: Before the scan, you may be asked to change into a gown and remove any metal objects or jewelry that could interfere with the MRI machine.
- Positioning: You’ll lie down on a movable table, which will gently slide into the MRI machine.
- Stillness: During the scan, it’s important to stay as still as possible to get clear images. The machine may make loud noises, but you’ll be given earplugs or headphones for comfort.
- Contrast Agent (If Needed): Sometimes, a special dye called a contrast agent is used to make certain structures show up better in the images. If needed, it will be given through a small needle in your arm.
- Comfort: While the MRI scan is generally comfortable, if you feel uneasy or claustrophobic, let the technologist know. They can help you feel more at ease.
FAQs
What scan is best for torn ligaments?
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan is usually the best imaging modality for visualizing and diagnosing torn ligaments.
Can ligament tear be seen in MRI scan?
Yes, ligament tears can be clearly visualized in an MRI scan, as it provides high-resolution images of soft tissues, including ligaments.
How do you confirm a torn ligament?
A torn ligament is often confirmed through clinical examination, patient history, and diagnostic imaging such as MRI. MRI is particularly effective in providing detailed information about ligament integrity.
Can I refuse contrast with my MRI?
Yes, you have the right to refuse contrast dye for your MRI. However, discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider, as contrast can enhance certain details in the images.
Which is better, MRI or MRI with contrast?
The need for contrast depends on the specific situation. A standard MRI can provide valuable information, but MRI with contrast can enhance details, making it beneficial for certain cases where additional clarity is needed. Your healthcare provider will determine which is best for your situation.
Read more on the side effect of an MRI scan.
Other topics you may be interested in:
| For further assistance call us on ☏08068172507 |

 Call us:
Call us:


 Call
Now
Call
Now